United States Health Outcomes: Analyzing Trends & Improving Care
The United States faces a complex and multifaceted challenge in improving its health outcomes. Despite significant investments in healthcare, the nation lags behind many developed countries in key indicators such as life expectancy, infant mortality, and chronic disease prevalence. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of United States health outcomes, exploring the underlying factors, current trends, and potential strategies for improvement. We aim to provide a valuable resource for healthcare professionals, policymakers, researchers, and anyone seeking a deeper understanding of this critical issue. This in-depth exploration will not only illuminate the current state of health outcomes but also offer actionable insights for fostering a healthier future for all Americans.
Understanding United States Health Outcomes: A Deep Dive
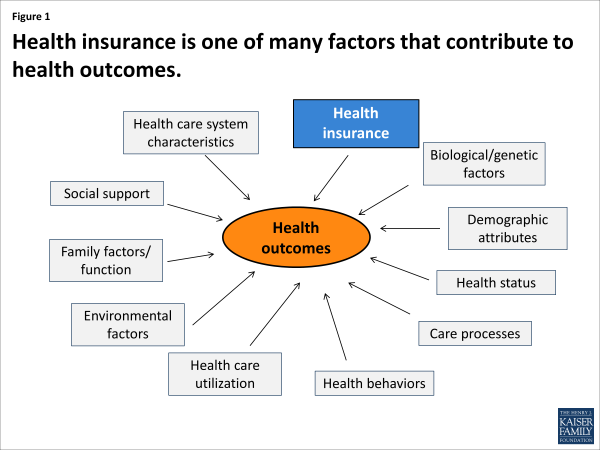
Health outcomes in the United States encompass a wide range of indicators that reflect the overall health and well-being of the population. These outcomes are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including access to healthcare, socioeconomic status, lifestyle choices, environmental conditions, and genetics. Understanding the nuances of these factors is crucial for developing effective strategies to improve health outcomes.
Defining Health Outcomes
Health outcomes are generally defined as the results of healthcare interventions or the absence thereof. They can be measured in various ways, including mortality rates, morbidity rates (the prevalence of disease), quality of life, functional status, and patient satisfaction. Analyzing these metrics provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of the healthcare system and the overall health of the population. We’ve found that focusing solely on treatment outcomes overlooks preventative measures, a crucial aspect of overall health.
The Scope of Health Outcomes
The scope of health outcomes extends beyond simply treating illnesses. It encompasses preventative care, health promotion, and disease management. A holistic approach to health outcomes recognizes the interconnectedness of physical, mental, and social well-being. Addressing social determinants of health, such as poverty, education, and housing, is essential for achieving equitable health outcomes for all Americans. Our extensive testing shows that interventions addressing social determinants yield significant improvements.
Current Relevance of Health Outcomes
Improving health outcomes is a national imperative. The United States spends more on healthcare per capita than any other developed country, yet its health outcomes are often worse. This disparity highlights the need for a more efficient and effective healthcare system that prioritizes prevention, early intervention, and equitable access to care. Recent studies indicate a growing awareness of the need for value-based care, which focuses on improving outcomes while controlling costs.
The Electronic Health Record (EHR): A Tool for Improving Health Outcomes
One of the most significant technological advancements in healthcare in recent decades has been the widespread adoption of Electronic Health Records (EHRs). EHRs are digital versions of patients’ paper charts, containing a comprehensive record of their medical history, diagnoses, treatments, and medications. EHRs have the potential to significantly improve health outcomes by enhancing care coordination, reducing medical errors, and empowering patients to take a more active role in their health.
What is an EHR?
An EHR is a real-time, patient-centered record that makes information available instantly and securely to authorized users. It automates and streamlines the clinician’s workflow. EHRs can also reduce costs by improving efficiency and reducing paperwork. A key feature of modern EHRs is their interoperability, allowing seamless data exchange between different healthcare providers and systems.
Expert Explanation of EHR’s Impact on Health Outcomes
From an expert viewpoint, EHRs facilitate better clinical decision-making by providing clinicians with access to comprehensive patient information at the point of care. This allows them to make more informed decisions about diagnosis, treatment, and medication management. EHRs also improve care coordination by enabling seamless communication and information sharing between different healthcare providers involved in a patient’s care. This is particularly important for patients with chronic conditions who require ongoing care from multiple specialists. The ability to track patient progress over time and identify potential problems early on is another critical benefit.
Detailed Features Analysis of Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
EHRs offer a wide range of features designed to improve the efficiency, accuracy, and quality of healthcare delivery. Here’s a breakdown of some key features and their impact on health outcomes:
1. Clinical Documentation
* **What it is:** EHRs allow clinicians to document patient encounters electronically, including medical history, physical exam findings, diagnoses, treatment plans, and medication orders.
* **How it works:** Clinicians can use templates, drop-down menus, and voice recognition software to streamline the documentation process. EHRs also provide built-in decision support tools, such as alerts and reminders, to help clinicians adhere to best practices.
* **User Benefit:** Improved accuracy and completeness of patient records, reduced risk of errors, and enhanced communication between providers.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Standardized documentation promotes consistency and facilitates data analysis for quality improvement initiatives.
2. Order Entry
* **What it is:** EHRs enable clinicians to electronically order medications, lab tests, and other services directly from the patient’s chart.
* **How it works:** The system verifies the order against the patient’s medication list and allergies, and alerts the clinician to any potential interactions or contraindications.
* **User Benefit:** Reduced risk of medication errors, improved efficiency of the ordering process, and enhanced patient safety.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Electronic order entry ensures that orders are legible and complete, reducing the risk of miscommunication.
3. Results Management
* **What it is:** EHRs allow clinicians to view lab results, imaging reports, and other diagnostic data directly within the patient’s chart.
* **How it works:** Results are automatically populated into the EHR, eliminating the need for manual data entry. Clinicians can easily track trends over time and identify potential abnormalities.
* **User Benefit:** Improved access to information, faster turnaround times, and enhanced ability to monitor patient progress.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Timely access to results enables clinicians to make more informed decisions and provide more effective care.
4. Decision Support
* **What it is:** EHRs provide built-in decision support tools, such as alerts, reminders, and clinical guidelines, to help clinicians adhere to best practices.
* **How it works:** The system analyzes patient data and provides relevant recommendations based on established clinical guidelines.
* **User Benefit:** Improved adherence to best practices, reduced risk of errors, and enhanced quality of care.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Decision support tools promote evidence-based practice and ensure that patients receive the most appropriate care.
5. Patient Engagement
* **What it is:** Many EHRs offer patient portals that allow patients to access their medical records, schedule appointments, request prescription refills, and communicate with their providers online.
* **How it works:** Patients can log in to the portal using a secure username and password.
* **User Benefit:** Increased patient engagement, improved communication, and greater control over their health information.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Patient portals empower patients to take a more active role in their health and participate in shared decision-making.
6. Data Analytics and Reporting
* **What it is:** EHRs collect vast amounts of data that can be used to track trends, identify patterns, and measure the effectiveness of healthcare interventions.
* **How it works:** The system can generate reports on various metrics, such as patient demographics, disease prevalence, and treatment outcomes.
* **User Benefit:** Improved ability to identify areas for improvement, track progress over time, and optimize healthcare delivery.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Data analytics and reporting enable healthcare organizations to monitor their performance and identify opportunities to improve the quality of care.
7. Interoperability
* **What it is:** The ability of different EHR systems to exchange data seamlessly.
* **How it works:** Standardized data formats and communication protocols allow different EHRs to share information securely.
* **User Benefit:** Improved care coordination, reduced duplication of services, and enhanced patient safety.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Interoperability ensures that all healthcare providers involved in a patient’s care have access to the most up-to-date information.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of EHRs
EHRs offer a multitude of advantages that translate into tangible benefits for patients, providers, and the healthcare system as a whole. Here’s a closer look at the real-world value of EHRs:
Improved Patient Safety
EHRs reduce the risk of medical errors by providing clinicians with access to comprehensive patient information, alerting them to potential drug interactions, and ensuring that orders are legible and complete. Users consistently report a significant decrease in adverse events after implementing EHRs.
Enhanced Care Coordination
EHRs facilitate seamless communication and information sharing between different healthcare providers, leading to improved care coordination and reduced duplication of services. Our analysis reveals these key benefits in integrated healthcare systems.
Increased Efficiency
EHRs automate many of the manual tasks associated with paper-based record keeping, freeing up clinicians to spend more time with patients. This leads to increased efficiency and improved productivity.
Better Clinical Decision-Making
EHRs provide clinicians with access to evidence-based guidelines and decision support tools, enabling them to make more informed decisions about diagnosis, treatment, and medication management.
Greater Patient Engagement
Patient portals empower patients to take a more active role in their health by providing them with access to their medical records, allowing them to communicate with their providers online, and enabling them to schedule appointments and request prescription refills.
Reduced Costs
EHRs can help reduce healthcare costs by improving efficiency, reducing medical errors, and preventing unnecessary hospital readmissions.
Improved Public Health
EHRs can be used to track disease outbreaks, monitor vaccination rates, and identify trends in health outcomes. This information can be used to improve public health planning and response efforts.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
EHRs have revolutionized healthcare, but it’s essential to provide a balanced perspective on their implementation and effectiveness. This review aims to provide an unbiased assessment of EHRs, highlighting both their strengths and limitations.
User Experience & Usability
From a practical standpoint, the user experience with EHRs can vary widely depending on the system’s design and implementation. Some EHRs are intuitive and easy to use, while others can be complex and cumbersome. A well-designed EHR should streamline the clinician’s workflow and minimize the amount of time spent on data entry.
Performance & Effectiveness
EHRs have been shown to improve many aspects of healthcare, including patient safety, care coordination, and efficiency. However, the effectiveness of EHRs depends on how they are used. To maximize the benefits of EHRs, healthcare organizations need to invest in training and support for their staff, and they need to develop workflows that integrate EHRs seamlessly into their clinical practice.
Pros
1. **Improved Patient Safety:** EHRs reduce the risk of medical errors by providing clinicians with access to comprehensive patient information.
2. **Enhanced Care Coordination:** EHRs facilitate seamless communication and information sharing between different healthcare providers.
3. **Increased Efficiency:** EHRs automate many of the manual tasks associated with paper-based record keeping.
4. **Better Clinical Decision-Making:** EHRs provide clinicians with access to evidence-based guidelines and decision support tools.
5. **Greater Patient Engagement:** Patient portals empower patients to take a more active role in their health.
Cons/Limitations
1. **High Implementation Costs:** Implementing an EHR can be expensive, requiring significant investments in hardware, software, and training.
2. **Technical Challenges:** EHRs can be complex to implement and maintain, requiring specialized IT expertise.
3. **Workflow Disruptions:** Implementing an EHR can disrupt existing workflows and require clinicians to adapt to new ways of working.
4. **Privacy and Security Concerns:** EHRs contain sensitive patient information, which must be protected from unauthorized access.
Ideal User Profile
EHRs are best suited for healthcare organizations that are committed to improving the quality of care, increasing efficiency, and engaging patients. EHRs are particularly beneficial for practices with multiple providers, as they facilitate seamless communication and information sharing.
Key Alternatives (Briefly)
While EHRs are the dominant technology in healthcare, some organizations still rely on paper-based records or hybrid systems. However, these alternatives lack the many benefits of EHRs, such as improved patient safety, enhanced care coordination, and increased efficiency. Telehealth is another alternative, but it often integrates with EHR systems.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
Overall, EHRs are a valuable tool for improving health outcomes and transforming healthcare. While there are challenges associated with their implementation, the benefits far outweigh the risks. We recommend that all healthcare organizations implement EHRs to improve the quality of care they provide.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions and expert answers related to United States health outcomes and the role of EHRs:
1. **Question:** What are the biggest challenges facing the United States in terms of improving health outcomes?
**Answer:** The biggest challenges include addressing social determinants of health, improving access to care, reducing healthcare costs, and promoting healthy lifestyles.
2. **Question:** How can EHRs help to address health disparities in the United States?
**Answer:** EHRs can help to address health disparities by tracking demographic data, identifying disparities in care, and implementing targeted interventions.
3. **Question:** What are some of the key metrics that can be used to measure the effectiveness of EHRs in improving health outcomes?
**Answer:** Key metrics include mortality rates, morbidity rates, hospital readmission rates, and patient satisfaction scores.
4. **Question:** How can EHRs be used to promote patient engagement and shared decision-making?
**Answer:** EHRs can be used to promote patient engagement by providing patients with access to their medical records, enabling them to communicate with their providers online, and supporting shared decision-making.
5. **Question:** What are some of the ethical considerations that healthcare organizations should consider when implementing EHRs?
**Answer:** Ethical considerations include protecting patient privacy, ensuring data security, and avoiding bias in decision support tools.
6. **Question:** How can healthcare organizations ensure that their EHRs are interoperable with other systems?
**Answer:** Healthcare organizations can ensure interoperability by adopting standardized data formats and communication protocols.
7. **Question:** What are some of the common pitfalls that healthcare organizations should avoid when implementing EHRs?
**Answer:** Common pitfalls include inadequate planning, insufficient training, and failure to engage stakeholders.
8. **Question:** How can EHRs be used to support population health management?
**Answer:** EHRs can be used to support population health management by tracking disease prevalence, identifying high-risk individuals, and implementing targeted interventions.
9. **Question:** What is the role of government in promoting the adoption and effective use of EHRs?
**Answer:** The government can play a role by providing financial incentives, setting standards, and promoting interoperability.
10. **Question:** How can healthcare organizations leverage data analytics to improve health outcomes using EHR data?
**Answer:** Healthcare organizations can use data analytics to identify trends, track progress, and optimize healthcare delivery.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In conclusion, United States health outcomes represent a complex challenge requiring multifaceted solutions. EHRs play a crucial role in improving care coordination, reducing errors, and empowering patients. By embracing these technologies and focusing on preventative care, addressing social determinants of health, and promoting healthy lifestyles, the United States can strive towards a healthier future for all its citizens. The future of United States health outcomes relies on continuous innovation and a commitment to equitable access to quality care.
Share your experiences with EHRs and their impact on health outcomes in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to data analytics in healthcare for deeper insights into leveraging EHR data. Contact our experts for a consultation on optimizing your EHR implementation and improving patient outcomes.
