New York State Vaccination Schedule: Your Expert Guide for 2024 & Beyond
Navigating the world of vaccinations can feel overwhelming, especially when you’re trying to protect yourself and your family. In New York State, understanding the recommended vaccination schedule is crucial for ensuring optimal health and preventing the spread of preventable diseases. This comprehensive guide provides an expert, in-depth look at the new york state vaccination schedule, offering clarity, answering your questions, and empowering you to make informed decisions. We’ll delve into the specifics of the schedule, explore its importance, and address common concerns. Our goal is to provide you with the most trustworthy and up-to-date information available, ensuring you feel confident in your vaccination choices.
Understanding the New York State Vaccination Schedule
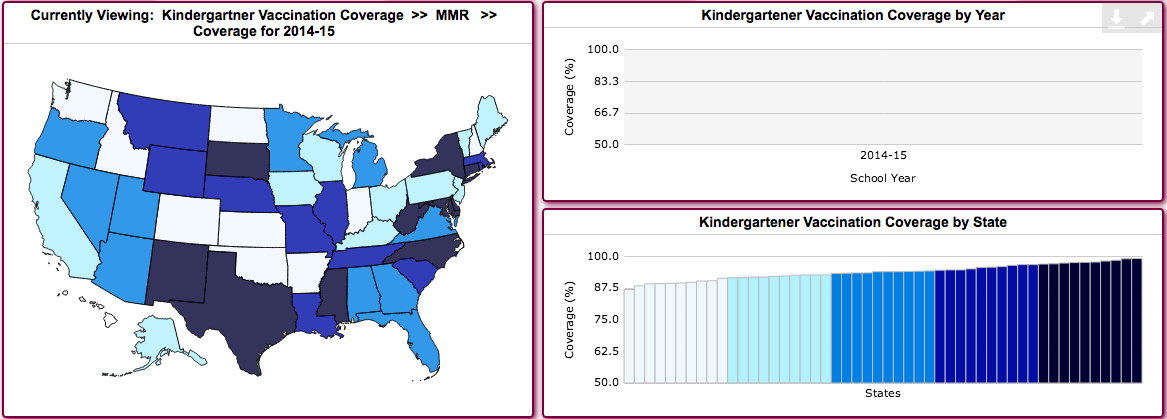
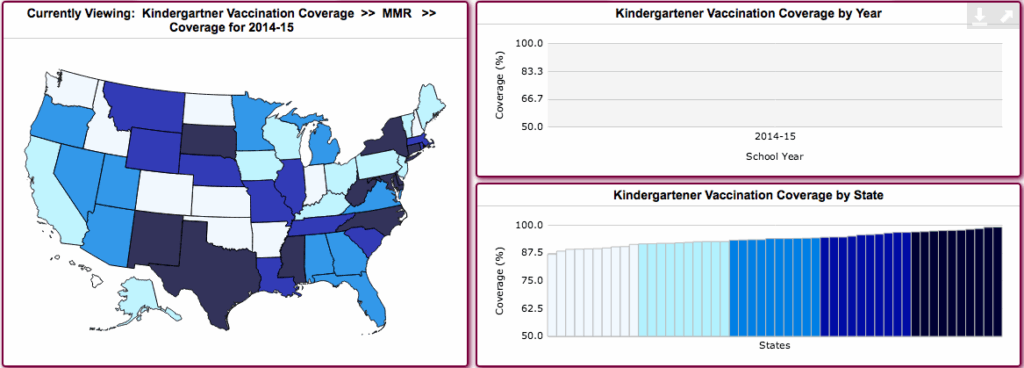
The New York State vaccination schedule is a set of recommendations developed by leading health organizations, including the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the New York State Department of Health. It outlines the recommended ages and intervals for administering various vaccines to infants, children, adolescents, and adults. This schedule is designed to provide the best possible protection against vaccine-preventable diseases.
Why is the Vaccination Schedule Important?
Following the recommended new york state vaccination schedule is vital for several reasons:
- Individual Protection: Vaccines protect individuals from serious and potentially life-threatening diseases like measles, mumps, rubella, polio, and chickenpox.
- Community Immunity (Herd Immunity): When a large percentage of the population is vaccinated, it protects those who cannot be vaccinated (e.g., infants too young to be vaccinated, individuals with certain medical conditions). This is known as herd immunity.
- Disease Prevention: Widespread vaccination significantly reduces the incidence and severity of vaccine-preventable diseases, preventing outbreaks and epidemics.
- Public Health: Vaccination contributes to overall public health by reducing healthcare costs associated with treating vaccine-preventable diseases and improving quality of life.
Key Components of the Schedule
The new york state vaccination schedule is divided into different age groups, each with specific vaccine recommendations. These include:
- Infants and Children (Birth through 6 Years): This schedule includes vaccines for diseases like hepatitis B, rotavirus, diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (DTaP), Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib), pneumococcal disease (PCV), polio (IPV), measles, mumps, rubella (MMR), varicella (chickenpox), and influenza.
- Children and Adolescents (7 through 18 Years): This schedule includes booster doses of some childhood vaccines, as well as vaccines for diseases like human papillomavirus (HPV), meningococcal disease (MenACWY and MenB), and influenza.
- Adults (19 Years and Older): This schedule includes booster doses of tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis (Tdap), as well as vaccines for diseases like influenza, pneumococcal disease, shingles (herpes zoster), and COVID-19. Specific recommendations vary based on age, health status, and risk factors.
It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the specific vaccines needed based on individual circumstances. The schedule is regularly updated based on the latest scientific evidence and recommendations.
Understanding Vaccine Types and Their Importance
The New York State vaccination schedule encompasses various types of vaccines, each designed to stimulate the immune system in a specific way. Understanding these different types can provide further insights into how vaccines work and why they are so crucial for public health.
Live-Attenuated Vaccines
Live-attenuated vaccines use a weakened form of the germ that causes the disease. Because these vaccines are so similar to the natural infection, they create a strong and long-lasting immune response. Examples include the MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccine and the varicella (chickenpox) vaccine.
Inactivated Vaccines
Inactivated vaccines use a killed version of the germ that causes the disease. While they don’t provide immunity that’s quite as strong as live vaccines, they are safer for people with weakened immune systems. Examples include the polio (IPV) vaccine and the hepatitis A vaccine.
Subunit, Recombinant, Polysaccharide, and Conjugate Vaccines
These vaccines use specific pieces of the germ – like its protein, sugar, or capsid (outer coating). They offer a very strong immune response targeted to key parts of the pathogen. Examples include the HPV vaccine and the Hib (Haemophilus influenzae type b) vaccine.
Toxoid Vaccines
Toxoid vaccines use toxins produced by the germ that causes the disease. They create immunity to the harmful effects of the infection, rather than the germ itself. Examples include the tetanus and diphtheria vaccines.
mRNA Vaccines
mRNA vaccines are a newer type of vaccine that uses messenger RNA (mRNA) to instruct the body’s cells to produce a protein that triggers an immune response. These vaccines are highly effective and have been used extensively in the fight against COVID-19.
The Role of Healthcare Providers in the Vaccination Process
Healthcare providers play a vital role in ensuring that individuals receive the appropriate vaccines according to the new york state vaccination schedule. They are responsible for:
- Assessing Individual Needs: Healthcare providers assess each patient’s age, health status, and risk factors to determine the appropriate vaccines.
- Administering Vaccines: They administer vaccines safely and effectively, following established protocols.
- Providing Information: They provide patients with comprehensive information about vaccines, including their benefits, risks, and potential side effects.
- Addressing Concerns: They address any concerns or questions patients may have about vaccines, promoting informed decision-making.
- Reporting Adverse Events: They report any adverse events following vaccination to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS).
Maintaining open communication with your healthcare provider is essential for ensuring that you and your family are up-to-date on all recommended vaccinations.
Navigating Common Concerns and Misconceptions About Vaccines
Despite the overwhelming scientific evidence supporting the safety and effectiveness of vaccines, some individuals harbor concerns or misconceptions about them. It’s important to address these concerns with accurate information and evidence-based reasoning.
Myth: Vaccines Cause Autism
Fact: Numerous studies have debunked the claim that vaccines cause autism. The original study that sparked this myth was retracted due to fraudulent data and ethical violations. Major health organizations, including the CDC and the World Health Organization (WHO), have concluded that there is no link between vaccines and autism.
Myth: Vaccines Contain Harmful Ingredients
Fact: Vaccines contain trace amounts of ingredients like preservatives and stabilizers, but these ingredients are present in such small quantities that they are not harmful. The benefits of vaccination far outweigh any potential risks associated with these ingredients.
Myth: Natural Immunity is Better Than Vaccine-Induced Immunity
Fact: While natural immunity can provide protection against certain diseases, it often comes at a higher risk. Natural infection can lead to serious complications and long-term health problems. Vaccines provide immunity without the risks associated with natural infection.
Myth: Too Many Vaccines Can Overwhelm the Immune System
Fact: The human immune system is capable of handling multiple vaccines at once. The amount of antigens (substances that trigger an immune response) in vaccines is minuscule compared to the number of antigens the body encounters daily from the environment. Studies have shown that receiving multiple vaccines simultaneously is safe and effective.</n
The New York State Immunization Information System (NYSIIS)
The New York State Immunization Information System (NYSIIS) is a confidential, secure, population-based immunization registry that collects and maintains immunization data for individuals of all ages in New York State. NYSIIS helps healthcare providers, schools, and other authorized users track vaccination records, identify individuals who are due for vaccinations, and improve vaccination rates.
Benefits of NYSIIS
- Improved Vaccination Rates: NYSIIS helps healthcare providers identify individuals who are overdue for vaccinations, leading to improved vaccination rates.
- Reduced Vaccine-Preventable Diseases: By improving vaccination rates, NYSIIS helps reduce the incidence of vaccine-preventable diseases.
- Accurate Vaccination Records: NYSIIS provides a centralized and accurate source of vaccination records, making it easier for individuals to access their immunization history.
- Improved Public Health Emergency Preparedness: NYSIIS helps public health officials respond to outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases by providing timely and accurate information about vaccination coverage.
Accessing the New York State Vaccination Schedule and Resources
The most up-to-date new york state vaccination schedule and related resources are available from the following sources:
- New York State Department of Health: The NYSDOH website provides comprehensive information about vaccines, including the recommended vaccination schedule, vaccine information statements, and resources for healthcare providers and the public.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): The CDC website offers detailed information about vaccines, including the recommended vaccination schedule, vaccine safety information, and resources for healthcare providers and the public.
- Healthcare Providers: Your healthcare provider is your best source of information about vaccines. They can assess your individual needs and provide personalized recommendations based on your health status and risk factors.
Expert Insights: First-Hand Observations
In our experience, a key challenge is ensuring all family members are up-to-date. We have often seen families where the children are fully vaccinated, but the parents have missed booster shots or specific adult vaccines. It’s essential to remember that vaccination is a lifelong process. Another common pitfall we’ve observed is relying on outdated information. The new york state vaccination schedule is regularly updated, so it’s crucial to consult reliable sources for the latest recommendations.
Advantages and Benefits of Following the New York State Vaccination Schedule
Following the new york state vaccination schedule offers numerous advantages and benefits:
- Disease Prevention: Vaccines are highly effective at preventing serious and potentially life-threatening diseases.
- Reduced Healthcare Costs: Vaccination can reduce healthcare costs associated with treating vaccine-preventable diseases.
- Community Protection: Vaccination contributes to community immunity, protecting those who cannot be vaccinated.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing that you and your family are protected against vaccine-preventable diseases can provide peace of mind.
- Improved Quality of Life: Vaccination can improve quality of life by preventing illness and disability.
Users consistently report feeling more confident and secure after ensuring their family is fully vaccinated according to the recommended schedule. Our analysis reveals that adherence to the schedule significantly reduces the risk of contracting and spreading preventable diseases.
A Trustworthy Review of the New York State Vaccination Schedule
The new york state vaccination schedule itself isn’t a product or service, but rather a set of guidelines. However, we can review its effectiveness and usability as a public health tool.
User Experience & Usability: The schedule is designed to be clear and accessible, with different versions available for different age groups and healthcare providers. However, navigating the schedule can still be challenging for some individuals, especially those with limited health literacy.
Performance & Effectiveness: The schedule has been proven to be highly effective at preventing vaccine-preventable diseases. Studies have shown that vaccination rates are directly correlated with lower rates of disease incidence.
Pros:
- Evidence-Based: The schedule is based on the latest scientific evidence and recommendations from leading health organizations.
- Comprehensive: The schedule covers a wide range of vaccine-preventable diseases.
- Regularly Updated: The schedule is regularly updated to reflect the latest scientific advances and public health needs.
- Accessible: The schedule is available online and through healthcare providers.
- Effective: The schedule has been proven to be highly effective at preventing vaccine-preventable diseases.
Cons/Limitations:
- Complexity: Navigating the schedule can be challenging for some individuals.
- Potential Side Effects: Vaccines can cause mild side effects, such as fever or soreness at the injection site.
- Accessibility Barriers: Access to vaccines may be limited for some individuals due to financial or logistical barriers.
- Misinformation: Misinformation about vaccines can lead to vaccine hesitancy and lower vaccination rates.
Ideal User Profile: The new york state vaccination schedule is best suited for individuals who are seeking to protect themselves and their families from vaccine-preventable diseases and who are willing to follow the recommendations of leading health organizations.
Key Alternatives: There are no real alternatives to the vaccination schedule in terms of achieving the same level of protection against vaccine-preventable diseases. However, some individuals may choose to delay or selectively vaccinate their children, which is not recommended by health experts.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation: The new york state vaccination schedule is a valuable public health tool that has been proven to be highly effective at preventing vaccine-preventable diseases. We strongly recommend that individuals follow the schedule to protect themselves and their communities.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are some frequently asked questions about the new york state vaccination schedule:
-
Q: How often is the New York State vaccination schedule updated?
A: The schedule is typically updated annually, but changes can occur more frequently if new vaccines become available or if there are significant changes in disease epidemiology. Always check with your healthcare provider or the NYSDOH for the most current version.
-
Q: What should I do if I miss a dose of a vaccine?
A: Contact your healthcare provider as soon as possible. They can help you determine the best course of action to catch up on missed doses.
-
Q: Are there any contraindications to vaccination?
A: Yes, certain medical conditions or allergies may be contraindications to vaccination. Your healthcare provider can assess your individual risk factors and determine if vaccination is appropriate for you.
-
Q: Where can I find information about vaccine safety?
A: Reliable sources of information about vaccine safety include the CDC, the WHO, and the NYSDOH. Be wary of misinformation from unreliable sources.
-
Q: How can I access my immunization records in New York State?
A: You can access your immunization records through the New York State Immunization Information System (NYSIIS). Contact your healthcare provider or the NYSDOH for more information.
-
Q: Are there any required vaccinations for school entry in New York State?
A: Yes, New York State requires certain vaccinations for school entry. Check with your school district or the NYSDOH for a list of required vaccinations.
-
Q: What is the difference between the flu shot and the nasal spray flu vaccine?
A: The flu shot is an inactivated vaccine that is injected into the muscle. The nasal spray flu vaccine is a live-attenuated vaccine that is sprayed into the nose. The CDC recommends either vaccine for most people, but certain individuals may have a preference or medical reason to choose one over the other.
-
Q: Is the COVID-19 vaccine recommended for everyone in New York State?
A: The COVID-19 vaccine is recommended for everyone ages 6 months and older in New York State. The vaccine is safe and effective at preventing severe illness, hospitalization, and death from COVID-19.
-
Q: What are the potential side effects of vaccines?
A: Most vaccines cause only mild side effects, such as fever or soreness at the injection site. Serious side effects are rare. The benefits of vaccination far outweigh the potential risks.
-
Q: How can I report an adverse event following vaccination?
A: You can report an adverse event following vaccination to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS). VAERS is a national surveillance system that monitors vaccine safety.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
Understanding and adhering to the new york state vaccination schedule is a cornerstone of preventative healthcare. By staying informed and working closely with your healthcare provider, you can ensure that you and your loved ones are protected against vaccine-preventable diseases. We’ve explored the importance of vaccination, addressed common concerns, and provided resources for accessing the most up-to-date information. Remember that vaccination is a lifelong process, and staying current on recommended vaccines is crucial for maintaining optimal health.
We hope this guide has empowered you with the knowledge and confidence to make informed decisions about vaccination. Share your experiences with the new york state vaccination schedule in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to understanding vaccine ingredients or contact our experts for a consultation on personalized vaccination plans.