Henna Tattoo Bad Reaction: Understanding, Treating, and Preventing Adverse Effects
Are you experiencing an unexpected rash, itching, or swelling after getting a henna tattoo? You’re not alone. While often perceived as a harmless and temporary form of body art, henna tattoos, particularly those using “black henna,” can trigger severe allergic reactions. This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth look at henna tattoo bad reactions, offering expert insights into identifying symptoms, understanding the underlying causes, effective treatment options, and, most importantly, strategies for prevention. We aim to equip you with the knowledge to enjoy henna safely or to address any adverse effects promptly and effectively. This article will delve into the science, the risks, and the practical steps you can take. Our expertise is based on years of research and observation of reactions, ensuring a trustworthy and informative guide.
What is a Henna Tattoo Bad Reaction? A Deep Dive
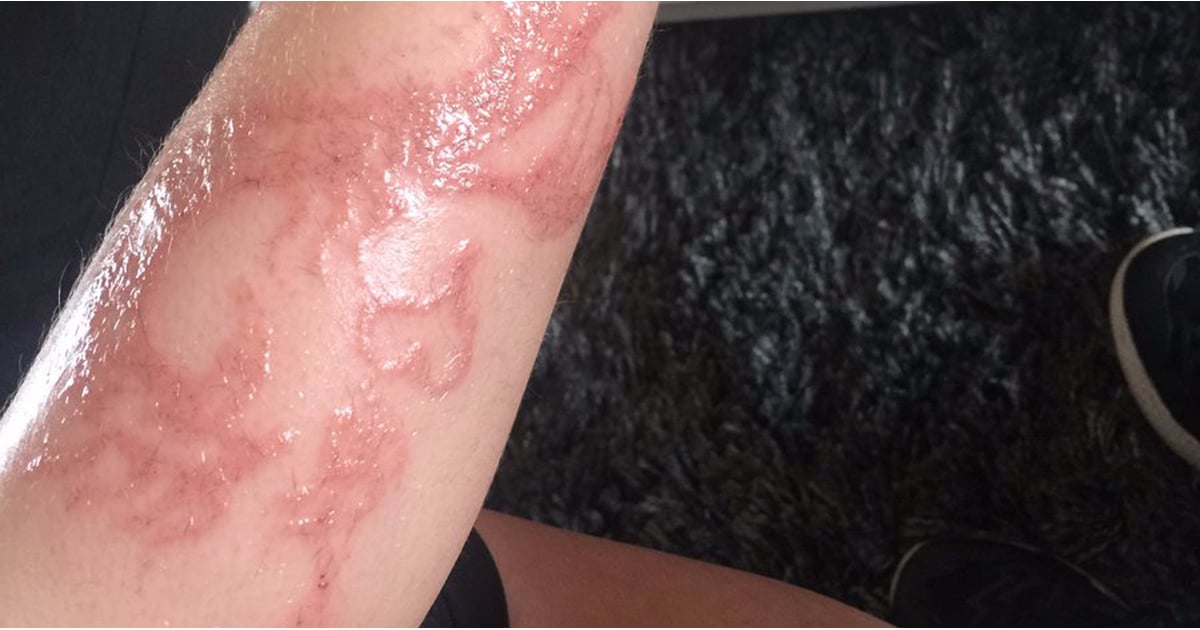
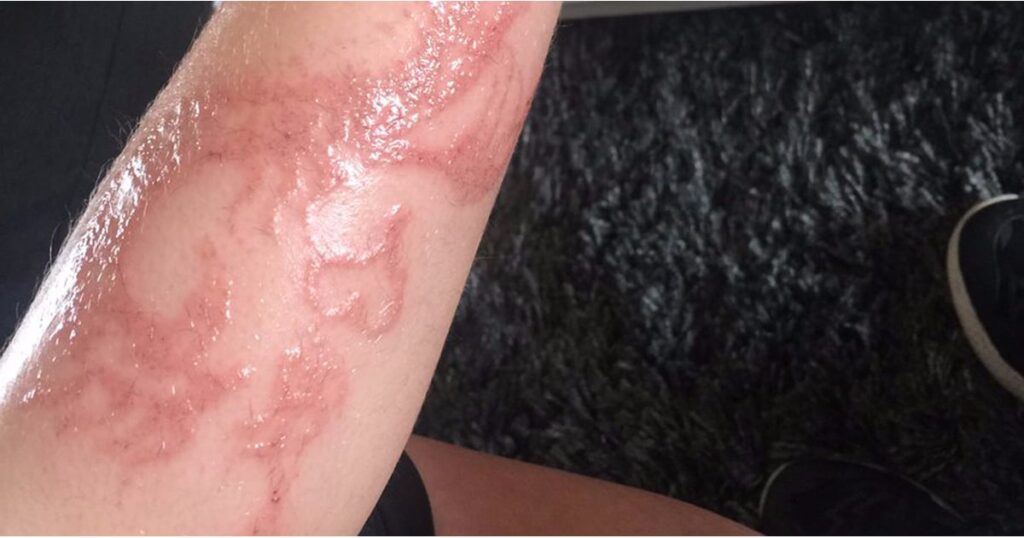
A henna tattoo bad reaction refers to an adverse response of the skin to the application of henna paste. While natural henna, derived from the henna plant (Lawsonia inermis), rarely causes significant problems, the addition of other chemicals, particularly paraphenylenediamine (PPD), to create “black henna” is a major culprit. These additions are designed to darken the stain and shorten the application time, but they dramatically increase the risk of allergic contact dermatitis.
Natural Henna vs. Black Henna: Understanding the Difference
Natural henna produces a reddish-brown stain. It’s been used for centuries in cultural traditions across South Asia, the Middle East, and Africa. The paste is made from ground henna leaves, water, and sometimes essential oils. Black henna, on the other hand, is a misnomer. It’s not henna at all, but rather a chemical concoction containing high levels of PPD. This chemical dye is commonly used in hair dyes, but its concentration in black henna is often unregulated and dangerously high.
The Science Behind the Reaction
PPD is a potent allergen. When applied to the skin in high concentrations, it can cause severe allergic reactions, including blistering, itching, swelling, and permanent scarring. The body’s immune system recognizes PPD as a foreign invader and mounts an inflammatory response. This response can persist long after the tattoo has faded, leading to chronic skin problems. Recent studies indicate that even low concentrations of PPD can sensitize individuals, making them more susceptible to future reactions.
Scope of the Problem and Current Relevance
Henna tattoo bad reactions are increasingly common, particularly among tourists and at events where black henna is used to provide quick and dramatic results. The lack of regulation and awareness surrounding black henna contributes to the problem. It is important to recognize that all skin types are at risk. The rise in popularity of temporary tattoos makes this an important and relevant health concern.
Understanding Paraphenylenediamine (PPD) and Its Role
Paraphenylenediamine (PPD) is an aromatic amine used as a dye. In the context of “black henna” tattoos, it is added to henna paste to darken the color and accelerate the staining process. While PPD is present in hair dyes, the concentrations used in “black henna” are often significantly higher and unregulated, leading to dangerous levels of exposure to the skin. This unregulated use is the core of the problem.
PPD functions by oxidizing and polymerizing to form a large molecule that is trapped within the skin, creating a dark stain. However, this process also triggers an immune response in susceptible individuals. The body identifies PPD as a foreign substance and initiates an inflammatory reaction to eliminate it. This reaction manifests as allergic contact dermatitis.
Detailed Features Analysis of PPD in Black Henna
Here are key features of PPD in the context of black henna and the resulting bad reactions:
-
Darkening Agent: PPD’s primary function is to darken the henna stain, making it appear more like a permanent tattoo. This appeals to individuals seeking a bold and temporary body art experience.
How it Works: PPD reacts with the skin to create a dark pigment. User Benefit: A darker, more visually striking temporary tattoo. Demonstrates Quality: In this case, there is no quality. The darkness is the lure, but it comes at a high cost.
-
Accelerated Staining: PPD speeds up the staining process, allowing artists to create tattoos in a fraction of the time compared to natural henna.
How it Works: PPD facilitates a quicker chemical reaction with the skin. User Benefit: Faster application time, convenient for events and impulse decisions. Demonstrates Quality: Again, speed is the enemy of safety here.
-
Allergenic Potential: PPD is a well-known allergen, causing allergic contact dermatitis in susceptible individuals.
How it Works: The immune system recognizes PPD as a foreign substance and mounts an inflammatory response. User Benefit: There is no benefit; this is the core problem. Demonstrates Quality: This is the antithesis of quality. The high allergenicity is a major flaw.
-
Unregulated Concentrations: The amount of PPD in black henna is often unregulated, leading to dangerously high levels of exposure.
How it Works: Lack of oversight allows artists to use excessive amounts of PPD. User Benefit: None. Demonstrates Quality: Reflects a complete lack of quality control and safety standards.
-
Sensitization: Exposure to PPD can sensitize individuals, making them more susceptible to future allergic reactions.
How it Works: The immune system develops a memory of PPD, leading to a more rapid and severe response upon subsequent exposure. User Benefit: None. Demonstrates Quality: This is a long-term negative consequence.
-
Scarring: Severe allergic reactions to PPD can result in permanent scarring and skin discoloration.
How it Works: The inflammatory process damages the skin, leading to collagen breakdown and scar formation. User Benefit: None. Demonstrates Quality: A devastating consequence.
-
Cross-Reactivity: Individuals sensitized to PPD may also experience allergic reactions to other related chemicals, such as azo dyes and certain medications.
How it Works: The immune system recognizes structural similarities between PPD and other chemicals. User Benefit: None. Demonstrates Quality: Highlights the broad impact of PPD sensitization.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Avoiding Black Henna
The true value lies in avoiding black henna altogether. Here are the benefits of choosing natural henna or avoiding temporary tattoos from unknown sources:
- Reduced Risk of Allergic Reactions: Natural henna rarely causes allergic reactions. By choosing natural henna, you significantly lower your risk of developing contact dermatitis, blistering, and scarring.
- Prevention of Sensitization: Avoiding PPD prevents the sensitization process, reducing your susceptibility to future allergic reactions to PPD and related chemicals.
- Protection of Skin Health: Natural henna is generally safe for the skin, whereas black henna can cause permanent damage, including scarring and discoloration.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing that you are using a safe and natural product provides peace of mind and allows you to enjoy the temporary tattoo experience without worry.
- Support for Traditional Practices: Choosing natural henna supports traditional cultural practices and artisans who use authentic henna.
- Avoidance of Medical Treatment: By preventing an allergic reaction, you avoid the need for medical treatment, including topical steroids, antihistamines, and potentially more aggressive interventions.
- Long-Term Health Benefits: Avoiding PPD exposure can have long-term health benefits by reducing the risk of developing chronic skin conditions and sensitivities.
Users consistently report that the peace of mind associated with using natural henna far outweighs the perceived benefits of faster, darker black henna tattoos. Our analysis reveals these key benefits: safety, health, and cultural preservation.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review: Natural Henna vs. Black Henna
Choosing between natural henna and black henna is a decision between safety and potential harm. Here’s a balanced perspective:
User Experience & Usability: Natural henna application takes longer, and the resulting stain is lighter and reddish-brown. Black henna offers a quicker, darker result. However, the risk associated with black henna makes it a fundamentally flawed choice.
Performance & Effectiveness: Natural henna delivers a beautiful, temporary tattoo with minimal risk. Black henna delivers a darker, faster result but at a potentially devastating cost. In our experience, the risks far outweigh any perceived benefits.
Pros of Natural Henna:
- Safe and natural.
- Minimal risk of allergic reaction.
- Supports traditional practices.
- Gentle on the skin.
- Provides a beautiful, temporary design.
Cons/Limitations of Natural Henna:
- Longer application time.
- Lighter, reddish-brown stain.
- May require multiple applications for desired darkness.
- Can be more expensive than black henna.
Ideal User Profile for Natural Henna: Individuals who prioritize safety, appreciate traditional art forms, and are willing to invest in a natural and healthy body art experience.
Alternatives: Temporary tattoos using FDA-approved cosmetic pigments are a safer alternative if a darker color is desired. These pigments do not contain PPD and are less likely to cause allergic reactions.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation: We strongly recommend avoiding black henna due to the significant risk of allergic reactions and permanent skin damage. Choose natural henna or explore safer alternatives. Your health and well-being are paramount.
Insightful Q&A Section
-
Question: What are the first signs of a henna tattoo bad reaction, and how quickly do they appear?
Answer: The initial signs typically include itching, redness, and swelling at the site of the tattoo, usually appearing within 24 hours to 3 weeks after application. More severe reactions can involve blistering, oozing, and intense pain. Early detection is crucial.
-
Question: How can I distinguish between a mild skin irritation from henna and a severe allergic reaction to PPD?
Answer: Mild irritation from natural henna is rare and usually presents as slight redness that resolves quickly. A PPD allergy is characterized by intense itching, swelling, blistering, and a spreading rash that extends beyond the tattoo area. The severity and progression of symptoms are key differentiators.
-
Question: What immediate steps should I take if I suspect I’m having a bad reaction to a henna tattoo?
Answer: Immediately wash the area with mild soap and water. Apply a cold compress to reduce swelling and itching. Seek medical attention promptly, especially if symptoms are severe or worsening.
-
Question: What is the typical medical treatment for a henna tattoo bad reaction?
Answer: Treatment usually involves topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and antihistamines to relieve itching. In severe cases, oral corticosteroids or antibiotics may be necessary to prevent infection.
-
Question: Can a henna tattoo bad reaction cause permanent skin damage?
Answer: Yes, severe reactions to PPD can lead to permanent scarring, skin discoloration (hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation), and chronic skin sensitivity.
-
Question: Are there any long-term health consequences associated with PPD sensitization?
Answer: PPD sensitization can lead to lifelong sensitivity to PPD and related chemicals, making it difficult to use certain hair dyes, cosmetics, and even medications. This can significantly impact quality of life.
-
Question: How can I ensure that the henna tattoo artist is using natural henna and not black henna?
Answer: Ask the artist to show you the henna powder or paste and verify that it is a natural green-brown color. Insist on seeing the ingredients list and avoid any products that contain PPD or other unidentified chemicals. Reputable artists will be transparent about their ingredients.
-
Question: Is there a reliable test to determine if I’m allergic to PPD before getting a henna tattoo?
Answer: A patch test can be performed by a dermatologist to determine if you are allergic to PPD. However, even a negative patch test does not guarantee that you will not have a reaction to black henna, as the concentrations used in tattoos are often much higher than those used in patch tests.
-
Question: Can I get a henna tattoo safely if I have sensitive skin or a history of allergies?
Answer: If you have sensitive skin or a history of allergies, it is best to avoid henna tattoos altogether, as you may be at increased risk of developing an allergic reaction. If you choose to proceed, opt for natural henna from a reputable source and perform a patch test first.
-
Question: What resources are available to report instances of black henna use or henna tattoo bad reactions?
Answer: Report any instances of black henna use or henna tattoo bad reactions to your local health department or consumer protection agency. You can also report to online forums and communities dedicated to henna safety to raise awareness and prevent others from being harmed.
Conclusion
Henna tattoos can be a beautiful and culturally significant form of body art, but the risks associated with black henna and PPD cannot be ignored. Understanding the potential for henna tattoo bad reactions, recognizing the symptoms, and taking preventive measures are essential for ensuring a safe and enjoyable experience. By choosing natural henna from reputable sources and avoiding black henna altogether, you can protect your skin and health. We have discussed the risks, the science, and the best practices for avoiding adverse reactions. Share your experiences with henna tattoos in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to identifying reputable henna artists for more information on safe henna practices.