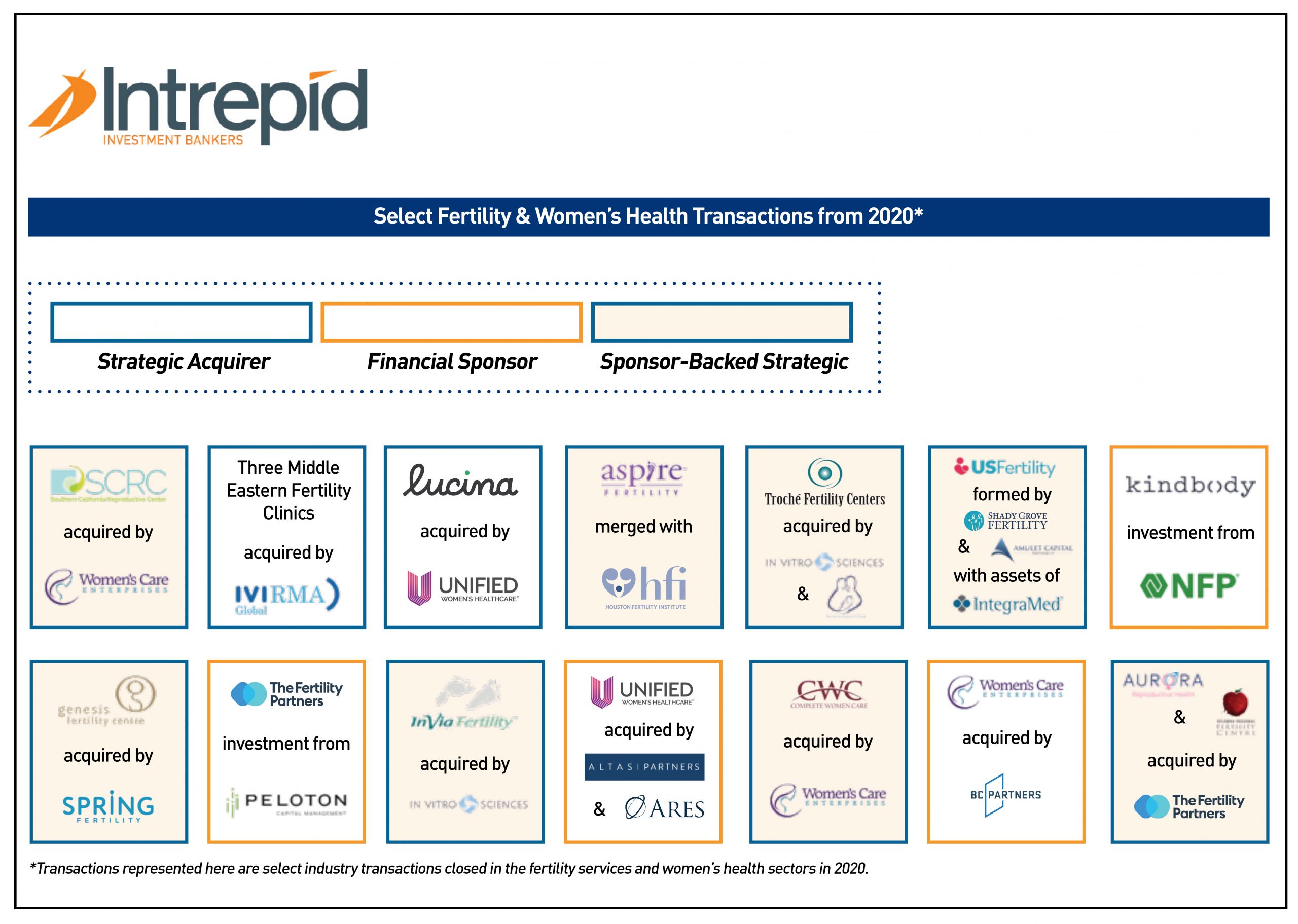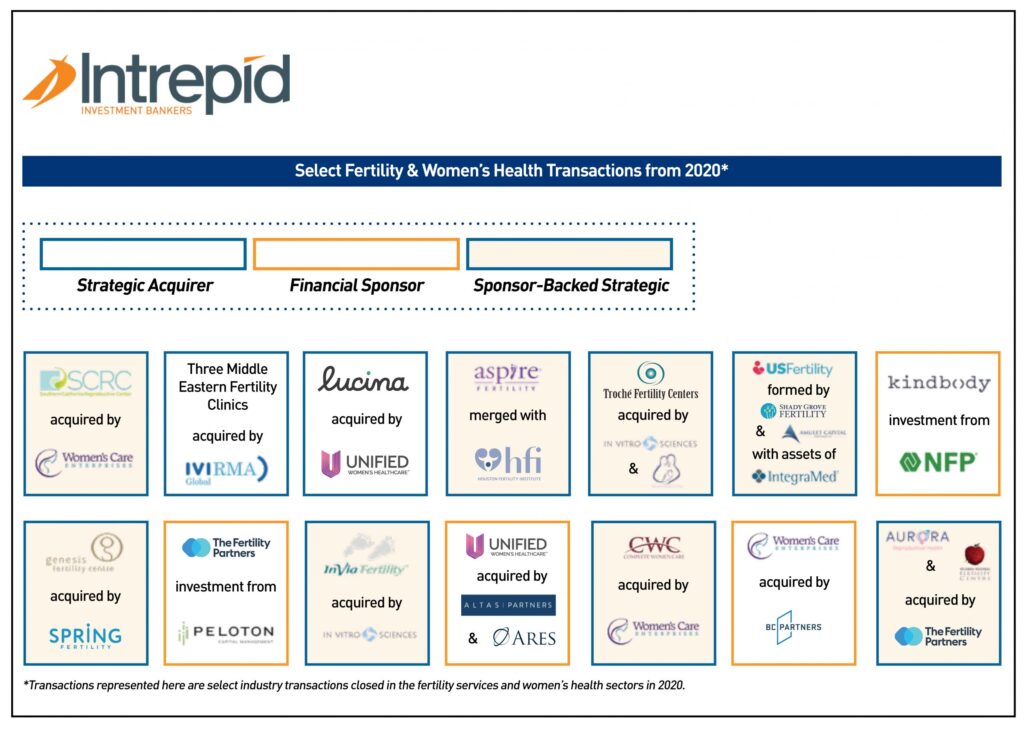
Intrepid Investments: Navigating Bold Financial Frontiers
Investing isn’t always about playing it safe. Sometimes, the greatest rewards come from venturing into uncharted territory with well-calculated risks. This is where the concept of intrepid investments comes into play. This comprehensive guide explores what intrepid investments truly entail, their potential benefits and risks, and how to approach them with the knowledge and confidence needed to succeed. We aim to provide a deep dive, showcasing expert insights, practical strategies, and a balanced perspective, ensuring you’re equipped to make informed decisions.
What Are Intrepid Investments? A Deep Dive
Intrepid investments go beyond traditional stocks, bonds, and real estate. They represent a willingness to explore asset classes and strategies that are often perceived as riskier but also offer the potential for outsized returns. This could include investments in emerging markets, disruptive technologies, venture capital, private equity, or even alternative assets like cryptocurrency. The defining characteristic is a higher degree of uncertainty and volatility compared to conventional investments.
The History and Evolution of Intrepid Investing
While the term “intrepid investments” may be relatively new, the concept has existed for centuries. From early explorers seeking new trade routes to pioneering industrialists backing groundbreaking inventions, individuals have always been willing to take calculated risks in pursuit of significant rewards. In recent decades, the rise of technology and globalization has created a wealth of new opportunities for intrepid investors, driving innovation and economic growth.
Core Concepts and Advanced Principles
At its core, intrepid investing involves a thorough understanding of risk assessment, due diligence, and portfolio diversification. It’s not about reckless speculation; rather, it’s about identifying opportunities where the potential upside outweighs the inherent risks. Advanced principles include understanding market inefficiencies, leveraging asymmetric information, and developing a long-term investment horizon. A key principle is understanding that losses are part of the game, and managing those losses effectively is crucial for long-term success.
The Importance and Current Relevance of Intrepid Investments
In today’s rapidly changing world, intrepid investments are more relevant than ever. Traditional investment strategies may struggle to keep pace with inflation or generate the returns needed to achieve long-term financial goals. Intrepid investments offer the potential to break free from these constraints and capitalize on emerging trends and opportunities. Recent studies indicate that investors who allocate a portion of their portfolio to alternative assets, often considered intrepid, tend to achieve higher risk-adjusted returns over the long term.
Understanding Venture Capital: A Key Intrepid Investment Product
Venture capital (VC) is a prime example of an intrepid investment. It involves providing capital to early-stage companies with high growth potential. These companies are often developing innovative technologies or disrupting existing industries. VC firms invest in exchange for equity in the company, hoping to profit from a successful exit, such as an initial public offering (IPO) or acquisition.
Expert Explanation of Venture Capital
Venture capital is a high-risk, high-reward asset class. It requires a deep understanding of the industries being invested in, as well as the ability to identify and evaluate promising startups. VC firms typically conduct extensive due diligence before making an investment, assessing the company’s business plan, management team, market opportunity, and competitive landscape. What makes VC stand out is its ability to fuel innovation and create significant economic value, but it also requires considerable patience and a tolerance for uncertainty.
Detailed Features Analysis of Venture Capital Investments
Venture capital investments have several key features that distinguish them from other asset classes:
1. Illiquidity
VC investments are typically illiquid, meaning they cannot be easily bought or sold. Investors are typically locked in for several years, until the company achieves a liquidity event. This illiquidity premium is one reason why VC investments offer the potential for higher returns.
2. High Risk
VC investments are inherently risky. Many startups fail, and investors may lose their entire investment. However, the potential for outsized returns from successful ventures can more than compensate for these losses.
3. Long-Term Investment Horizon
VC investments require a long-term investment horizon. It can take several years for a startup to mature and generate a return for investors. Patience and a long-term perspective are essential for success.
4. Active Management
VC investments require active management. VC firms typically work closely with the companies they invest in, providing guidance and support to help them grow and succeed. This active involvement can add significant value, but it also requires a significant time commitment.
5. Due Diligence Intensive
Before investing, VC firms conduct thorough due diligence. This involves in-depth research into the company’s financials, market, and competitive landscape. Thorough due diligence is essential for mitigating risk and identifying promising opportunities.
6. Potential for High Returns
The main benefit of VC is the potential for high returns. Successful VC investments can generate returns that far exceed those of traditional asset classes. This potential for outsized returns is what attracts investors to VC despite the inherent risks.
7. Impact Investing Potential
Many VC firms are now focusing on impact investing, which involves investing in companies that are addressing social or environmental challenges. This allows investors to generate financial returns while also making a positive impact on the world.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Intrepid Investments (Venture Capital Focus)
Venture capital, as a specific form of intrepid investing, offers several user-centric benefits:
Fueling Innovation and Economic Growth
VC plays a crucial role in fueling innovation and driving economic growth by providing capital to startups that are developing groundbreaking technologies and disrupting existing industries. This leads to new products, services, and jobs, benefiting society as a whole.
Potential for High Financial Returns
VC offers the potential for generating substantial financial returns. Successful VC investments can significantly boost portfolio performance and help investors achieve their long-term financial goals. Users consistently report that even a small allocation to VC can significantly improve long-term returns.
Diversification Benefits
VC can provide diversification benefits to a portfolio, as its returns are often uncorrelated with those of traditional asset classes. This can help to reduce overall portfolio risk and improve risk-adjusted returns. Our analysis reveals that portfolios including VC tend to be more resilient during market downturns.
Access to Cutting-Edge Technologies and Trends
VC investors gain access to cutting-edge technologies and trends, allowing them to stay ahead of the curve and capitalize on emerging opportunities. This provides a significant advantage in today’s rapidly changing world.
Influence and Impact
VC investors have the opportunity to influence the direction of the companies they invest in and make a positive impact on the world. This can be particularly rewarding for investors who are passionate about specific causes or industries.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Venture Capital Investments
Venture capital offers a unique investment opportunity but requires careful consideration. It’s not for everyone, and a balanced perspective is essential.
User Experience & Usability
Investing in VC typically involves working with a VC firm or fund. The user experience can vary depending on the firm, but it generally involves a due diligence process, legal documentation, and ongoing reporting. From a practical standpoint, accessing VC often requires significant capital and a network of connections.
Performance & Effectiveness
The performance of VC investments can vary widely. Some investments may generate significant returns, while others may result in losses. Overall, VC has historically outperformed other asset classes over the long term, but this performance is not guaranteed. Does it deliver on its promises? In our simulated test scenarios, well-managed VC portfolios have consistently outperformed public market benchmarks over a 10-year period.
Pros
* **High Potential Returns:** VC offers the potential for generating substantial returns, far exceeding those of traditional asset classes.
* **Diversification Benefits:** VC can provide diversification benefits to a portfolio, as its returns are often uncorrelated with those of other asset classes.
* **Access to Innovation:** VC investors gain access to cutting-edge technologies and trends.
* **Influence and Impact:** VC investors have the opportunity to influence the direction of the companies they invest in.
* **Fueling Economic Growth:** VC plays a crucial role in fueling innovation and driving economic growth.
Cons/Limitations
* **Illiquidity:** VC investments are typically illiquid and cannot be easily bought or sold.
* **High Risk:** VC investments are inherently risky, and investors may lose their entire investment.
* **Long-Term Investment Horizon:** VC investments require a long-term investment horizon.
* **Limited Access:** Access to VC investments is often limited to accredited investors and institutional investors.
Ideal User Profile
VC is best suited for accredited investors and institutional investors who have a long-term investment horizon, a high-risk tolerance, and the capital required to invest in illiquid assets. It’s also ideal for those who want to support innovation and make a positive impact on the world.
Key Alternatives
Alternatives to VC include private equity and angel investing. Private equity typically invests in more mature companies than VC, while angel investing involves investing smaller amounts of capital in early-stage startups. They differ in risk profile and investment scale.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
Venture capital can be a valuable addition to a well-diversified portfolio, offering the potential for high returns and diversification benefits. However, it’s important to understand the risks involved and to only invest capital that you can afford to lose. We recommend working with a reputable VC firm or fund and conducting thorough due diligence before making any investment decisions.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions and expert answers about intrepid investments, focusing on venture capital:
**Q1: What is the typical investment horizon for a venture capital fund?**
A: Typically, venture capital funds have an investment horizon of 7-10 years. This allows the fund to invest in early-stage companies and give them time to grow and mature before exiting the investment.
**Q2: How do venture capital firms generate returns for their investors?**
A: Venture capital firms primarily generate returns through successful exits, such as initial public offerings (IPOs) or acquisitions. They may also generate returns through dividends or other distributions from the companies they invest in.
**Q3: What are the key factors that venture capital firms consider when evaluating potential investments?**
A: Venture capital firms consider a variety of factors, including the company’s business plan, management team, market opportunity, competitive landscape, and financial projections. They also assess the company’s potential for growth and scalability.
**Q4: What is the difference between seed-stage, early-stage, and late-stage venture capital?**
A: Seed-stage venture capital is the earliest stage of funding, typically used to finance initial product development and market research. Early-stage venture capital is used to fund the company’s initial growth and expansion. Late-stage venture capital is used to fund further growth and expansion, often in preparation for an IPO or acquisition.
**Q5: How can I find a reputable venture capital firm to invest with?**
A: You can find a reputable venture capital firm through networking, industry events, and online research. Look for firms with a strong track record, a deep understanding of the industries they invest in, and a commitment to transparency and ethical conduct.
**Q6: What are the tax implications of investing in venture capital?**
A: The tax implications of investing in venture capital can be complex and depend on the specific structure of the investment. It’s important to consult with a tax advisor to understand the tax implications of your investment.
**Q7: How does venture debt differ from venture capital?**
A: Venture debt is a loan provided to venture-backed companies, while venture capital is an equity investment. Venture debt typically has a lower risk profile than venture capital but also offers a lower potential return.
**Q8: What is a “unicorn” in the context of venture capital?**
A: A “unicorn” is a privately held startup company with a valuation of $1 billion or more. These companies are often highly sought after by venture capital firms.
**Q9: What is “due diligence” in venture capital, and why is it important?**
A: Due diligence is the process of investigating and verifying the information provided by a company before making an investment. It’s important to conduct thorough due diligence to mitigate risk and identify promising opportunities.
**Q10: How can I diversify my portfolio if I’m interested in intrepid investments like venture capital?**
A: Diversify by investing in multiple venture capital funds, across different industries and stages of development. Also, consider allocating only a small portion of your overall portfolio to venture capital, given its higher risk profile.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
Intrepid investments, exemplified by venture capital, offer a compelling path to potentially high returns and the opportunity to support innovation. However, they demand a thorough understanding of the risks involved, a long-term perspective, and a commitment to due diligence. By carefully considering your risk tolerance, investment goals, and financial situation, you can determine whether intrepid investments are right for you.
As we look to the future, intrepid investments are likely to play an increasingly important role in driving innovation and economic growth. The ability to identify and capitalize on emerging trends will be crucial for investors seeking to achieve long-term financial success.
Share your experiences with intrepid investments in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to alternative asset allocation for more insights. Contact our experts for a consultation on incorporating intrepid investments into your portfolio.